|
Medicine RSS-Feeds by Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com
Πληροφορίες
Δευτέρα 23 Νοεμβρίου 2020
PREselection of Patients at Risk for COgnitive DEcline After Radiotherapy Using Advanced MRI
OH2 Oncolytic Viral Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer
|
Silicon Microsieve Device vs Cell Surface Marker-based Platform for the Isolation of Pancreatic Cancer CTCs
|
A Study to Evaluate Camrelizumab Plus Apatinib as Adjuvant Therapy in Patients With HCC at High Risk of Recurrence After Surgical Resection or Ablation
|
Fluorescence Molecular Endoscopy and Molecular Fluorescence-guided Surgery in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
|
Identification and validation of a six-gene signature associated with glycolysis to predict the prognosis of patients with cervical cancer
|
Risk stratification for prediction of locoregional recurrence in patients with pathologic T1–2N0 breast cancer after mastectomy
|
Association between five types of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α gene polymorphism and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: a meta-analysis
|
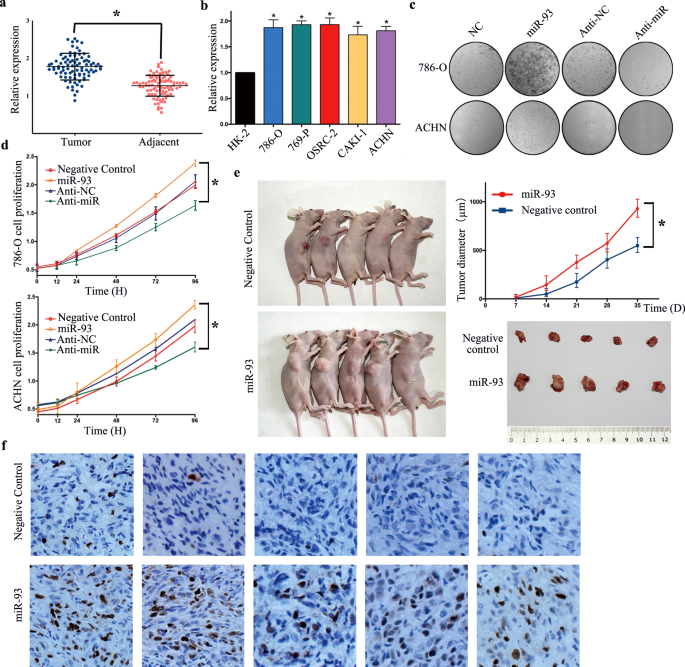
STAT3 regulates miR93-mediated apoptosis through inhibiting DAPK1 in renal cell carcinoma
|
Genomics and prognosis analysis of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer patients
|
Overriding sorafenib resistance via blocking lipid metabolism and Ras by sphingomyelin synthase 1 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma
|
Development and validation of an RNA binding protein-associated prognostic model for hepatocellular carcinoma
|
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(366)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (184)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (182)
-
►
2022
(2814)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (182)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (213)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (264)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (262)
-
►
2021
(3815)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (229)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (276)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (64)
-
▼
2020
(5754)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (401)
-
▼
Νοεμβρίου
(552)
-
▼
Νοε 23
(25)
- PREselection of Patients at Risk for COgnitive DEc...
- OH2 Oncolytic Viral Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer
- Silicon Microsieve Device vs Cell Surface Marker-b...
- A Study to Evaluate Camrelizumab Plus Apatinib as ...
- Fluorescence Molecular Endoscopy and Molecular Flu...
- Identification and validation of a six-gene signat...
- Risk stratification for prediction of locoregional...
- Association between five types of Tumor Necrosis F...
- STAT3 regulates miR93-mediated apoptosis through i...
- Genomics and prognosis analysis of epithelial-mese...
- Overriding sorafenib resistance via blocking lipid...
- Development and validation of an RNA binding prote...
- STAT3 regulates miR93-mediated apoptosis through i...
- Optimizing the use of telemedicine in oncology car...
- Safety and clinical activity of a new anti-PD-L1 a...
- Combined Inhibition of G{alpha}q and MEK Enhances ...
- Therapeutic potential of NTRK3 inhibition in desmo...
- Recommendation regarding the cranial upper border ...
- Impact of prior cancer history on the survival of ...
- Whole-brain irradiation differentially modifies ne...
- The impact of lifecourse socio-economic position a...
- High cumulative doxorubicin dose for advanced soft...
- Bladder cancer stage and mortality: urban vs. rura...
- Circ-ZNF124 downregulation inhibits non-small cell...
- Weekly versus triweekly cisplatin-alone adjuvant c...
-
▼
Νοε 23
(25)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (365)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (754)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (894)
-
►
2019
(146)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)