Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 924: PD-L1–PD-1 Pathway in the Pathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma
Cancers doi: 10.3390/cancers12040924
Authors:
Hideto Tamura
Mariko Ishibashi
Mika Sunakawa-Kii
Koiti Inokuchi
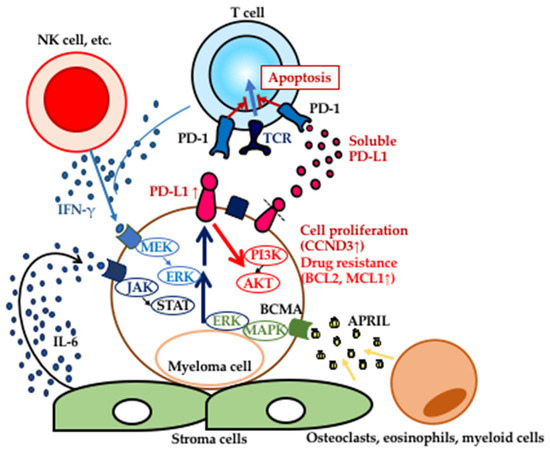
PD-L1 expressed on tumor cells contributes to disease progression with evasion from tumor immunity. Plasma cells from multiple myeloma (MM) patients expressed higher levels of PD-L1 compared with healthy volunteers and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) patients, and its expression is significantly upregulated in relapsed/refractory patients. Furthermore, high PD-L1 expression is induced by the myeloma microenvironment and PD-L1+ patients with MGUS and asymptomatic MM tend to show disease progression. PD-L1 expression on myeloma cells was associated with more proliferative potential and resistance to antimyeloma agents because of activation of the Akt pathway through PD-1-bound PD-L1 in MM cells. Those data suggest that PD-L1 plays a crucial role in the disease progression of MM.

Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου